Raji Cells - Unlocking Lymphoma Insights
First isolated in 1963 by R.J.V. Pulvertaft from a case of Burkitt's lymphoma, Raji cells have become a cornerstone in the study of lymphoma and immunology. These cells, characterized by their lymphoblast-like appearance and high CD19 expression—a key regulator of B-cell receptor signaling—are pivotal for delving into the intricacies of lymphoma and for testing new therapeutic strategies. As non-adherent cells that proliferate in free-floating aggregates, Raji cells are particularly noted for their utility in evaluating immunotherapeutic approaches, including their application in studying bispecific antibodies aimed at treating non-Hodgkin’s B cell lymphoma. Additionally, their BCMA expression makes them invaluable in multiple myeloma research, underlining their broad applicability and crucial role in advancing cancer research.
Overview of Raji Cell Line Characteristics and Origin
Understanding a cell line's fundamental attributes and origins is critical before commencing research. This section provides insights into Raji cells, including their derivation, morphology, and key features.
- Derived from the left maxilla of an 11-year-old Nigerian boy with Burkitt lymphoma, the Raji cell line was established by R.J.V. Pulvertaft in 1963, offering a unique window into B-cell lymphomas.
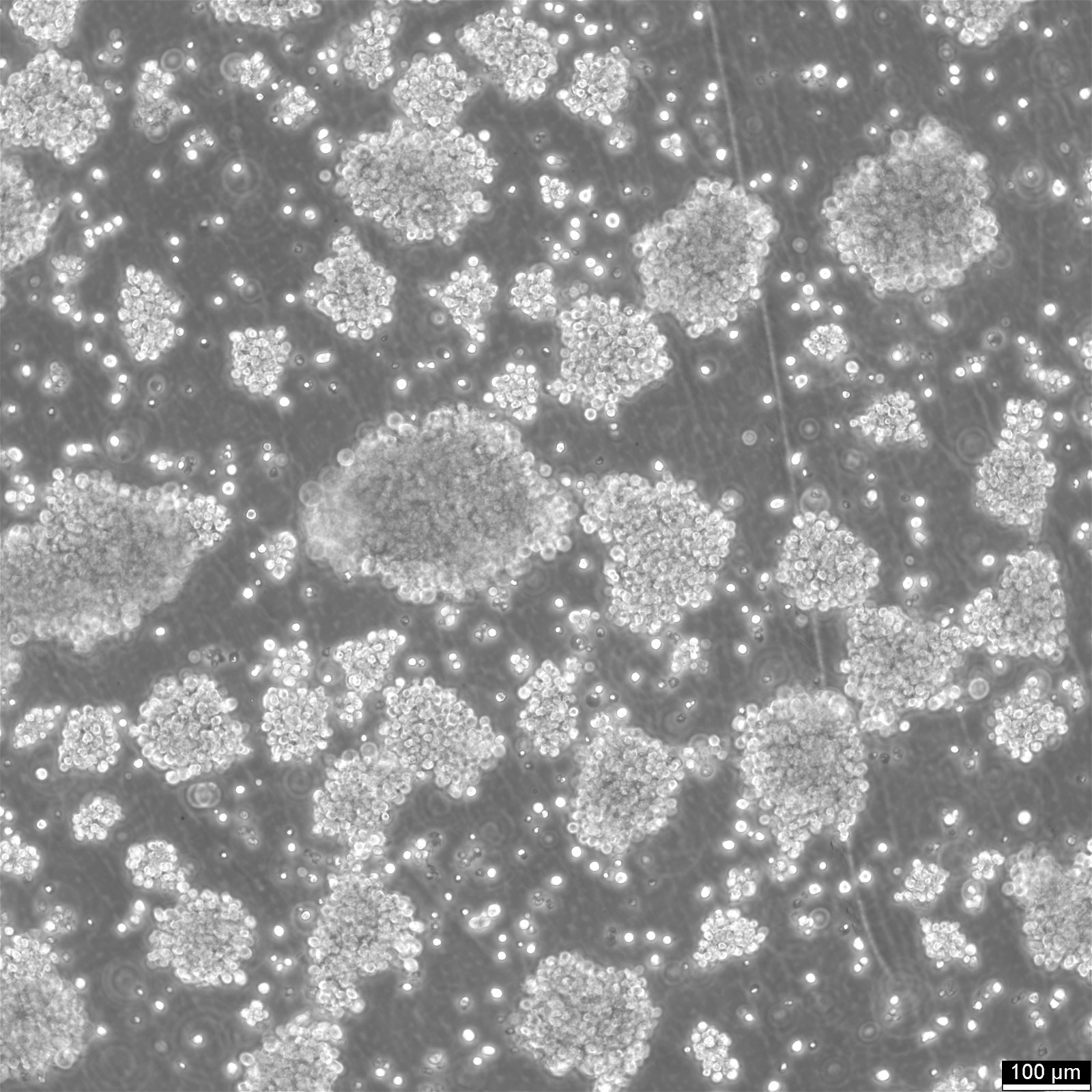
- Raji cells thrive as suspension cultures, typically forming clusters that can vary in size and density, illustrating their adaptability in vitro.
- These cells are distinguished by their small diameter (5-8 μm), extensive cytoplasm, and a uniquely indented nucleus, contributing to their distinct lymphoblast-like morphology.
- With a stable karyotype and a diploid chromosome number, Raji cells provide a consistent model for genetic studies within cancer research.
Culturing Raji Cells
Mastering the cultivation of a cell line such as Raji cells demands familiarity with their specific culturing requirements. Essential aspects to consider include their doubling time, preferred culture media, growth nature (suspension or adherent), optimal seeding density, and necessary biosafety precautions.
Key Points for Culturing Raji Cells
Population Doubling Time: Raji cells have a population doubling time of approximately 23.2 hours, necessitating regular monitoring to maintain optimal cell health.
Growth Nature: Characteristically, Raji cells proliferate in suspension, forming dynamic clusters that highlight their lymphoblast-like nature.
Seeding Density: For optimal growth, the initial seeding density is maintained at 1-2 x 105 cells/ml. Since Raji cells grow in suspension, they do not require detachment solutions but are instead diluted directly into the culture medium at the desired density.
Culture Medium: The recommended medium for Raji cells is RPMI 1640, enhanced with 2.0 mM L-glutamine, 2.0 g/L L-glucose, 2.0 g/L NaHCO3, and 10% fetal bovine serum (FBS) to support robust cell growth.
Optimal Growth Conditions: Raji cells thrive in a controlled environment at 37°C with 5% CO2 in a humidified incubator, mirroring their physiological conditions.
Cell Storage: For long-term preservation, Raji cells are stored in the vapor phase of liquid nitrogen at temperatures below -150°C, ensuring sustained cell viability.
Freezing Protocol: Employing CM-1 or CM-ACF as freezing media, Raji cells are best preserved using a gradual cooling process to minimize cellular stress and maintain viability.
Thawing Raji Cells: Thawing involves briefly warming the cells in a 37°C water bath until a small ice clump remains. Post-thaw, cells are gently resuspended in fresh culture media and either centrifuged to remove the freezing medium or directly transferred to new flasks with a subsequent media change after 24 hours to remove any residual freezing media.
Biosafety Considerations: Culturing Raji cells necessitates adherence to biosafety level 1 guidelines, ensuring safe handling and maintenance practices within the laboratory.
Understanding and implementing these key culturing practices will facilitate the successful growth and maintenance of Raji cells, enabling their effective use in lymphoma research and beyond.
Raji: Pioneering Advances in Research
- Cancer Research Insights: Originating from Burkitt's lymphoma, Raji cells are indispensable in the realm of cancer research, particularly for dissecting the complexities of B-cell malignancies. These cells are instrumental in investigating the ramifications of p53 gene mutations, a hallmark in the progression of numerous cancers. This exploration is crucial for unveiling potential resistance mechanisms to current treatments and paving the way for novel therapeutic strategies. The versatility of Raji cells extends their utility beyond Burkitt lymphoma, offering a broader perspective on hematological malignancies and enriching our oncological treatment arsenal.
- Immunological Innovations: In immunology, the significance of Raji cells cannot be overstated, attributed to their expression of key surface molecules integral to immune functionality. Employed in the renowned Raji cell assay, these cells provide a window into the interactions between immune complexes and B-cells. Understanding these interactions is essential for unraveling the mechanisms of immune evasion by cancer cells, thereby informing the development of groundbreaking immunotherapies and vaccines targeting leukemia and other B-cell disorders.
Unlocking Research Potential: Top Raji Cell Lines for Your Laboratory
Highlighted Studies Featuring Raji Cells
- Exploring the Anti-Cancer Potential of Meloxicam on Raji Cells: A 2022 study in the International Journal of Dentistry examines the impact of Meloxicam on Raji lymphoma cells, showcasing its prowess in cell proliferation inhibition and apoptosis induction.
- Combining Forces: CD19 CAR-T Cells and Ibrutinib Against Raji Cells: This 2020 Cancer Science article delves into the synergistic effects of CD19 CAR-T cell therapy and the drug ibrutinib on Raji cells, demonstrating a potentiated anti-lymphoma action.
- Targeting lncRNA PVT1 in Raji Cells: A Strategy to Curb Proliferation Highlighted in a 2019 Oncology Letters publication, the study reveals how lncRNA PVT1 knockdown can effectively reduce Raji cell proliferation, offering insights into cell cycle regulation.
- Disrupting the JAK2/STAT3 Pathway in Raji Cells: A Path to Inhibit Proliferation A 2018 Medical Science Monitor study focuses on the impact of JAK2/STAT3 pathway inhibition in Raji cells, with implications for proliferation, apoptosis, and oxidative stress management.
- Deciphering EBV Entry into NK Cells: Raji and NK Cell Coculture Insights An intriguing 2018 Cellular Immunology publication investigates the entry of the Epstein-Barr virus into NK cells independent of the CD21 receptor, using Raji and NK cell cocultures to shed light on virus-cell dynamics.
Frequently Asked Questions
p53 mutations can influence the behavior of Raji cells, often leading to altered cell cycle control and contributing to the aggressive nature of other Burkitt lymphoma cells.
Studying DC inhibition helps understand how Raji cells interact with the immune system, which is crucial in molecular biology and immunology research.
Raji cells are often used to study EBV, as they are derived from a lymphoma that is frequently associated with the virus.
While primarily associated with lymphoma, Raji cells can provide insights into tumor biology more broadly.
Raji cells serve as a model to study Burkitt lymphoma, allowing for investigation into the pathology of the disease.
Raji cells express specific surface proteins that can be targeted for cancer treatment research.
While primarily associated with lymphoma, Raji cells can provide insights into tumor biology more broadly.
Enhanced Resources for Raji Cell Line Research
Discover a curated selection of resources designed to facilitate Raji cell line research, including detailed protocols for culturing, freezing, and subculturing:
- Comprehensive Raji Cell Protocols: Access a detailed guide on the essential protocols for the freezing, thawing, and splitting of Raji cells, providing step-by-step instructions to ensure optimal cell viability and performance.
- Subculturing Suspension Cells Tutorial: Watch this informative video to learn the best practices for subculturing suspension cells, including techniques relevant to Raji cell maintenance.
- Raji Cell Culturing Insights: Explore this resource for valuable information on Raji cell culture media, optimal freezing media, and subculturing protocols tailored for the unique requirements of these lymphoma cells.